
MICHAEL PORTER!
COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE
Competitive advantage is a business concept describing attributes that allow an organization to outperform itscompetitors. These attributes may include access to natural resources, such as high grade ores or inexpensive power, highly skilled personnel, geographic location, high entry barriers, etc. New technologies, such as robotics and information technology, can also provide competitive advantage, whether as a part of the product itself, as an advantage to the making of the product, or as a competitive aid in the business process (for example, better identification and understanding of customers).
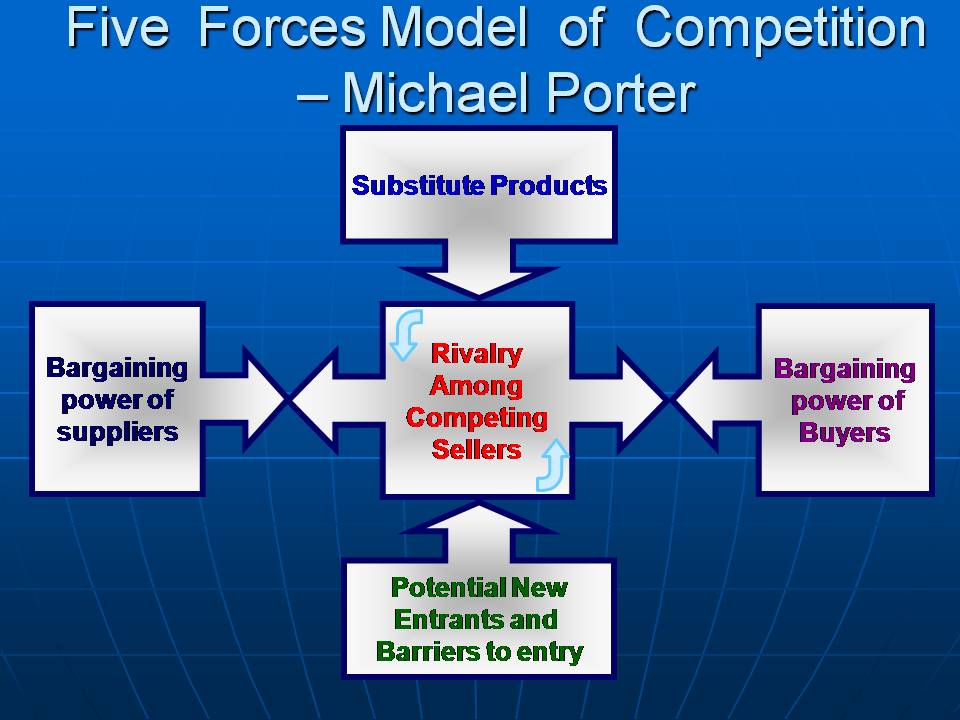
BUYER POWER
¡High –
when buyers have many choices of whom to buy.
¡Low –
when their choices are few.
¡To
reduce buyer power (and create competitive advantage), an organization must
make it more attractive to buy from the company not from the competitors.
¡Best
practices of IT-based
High – when buyers have few choices of whom to buy from.
Low – when their choices are many.
-Best practices of IT to create competitive advantage.
-E.g. B2B marketplace – private exchange allow a single buyer to posts it needs and then open the
bidding to any supplier who would care to bid. Reverse auction is an auction format in which increasingly lower bids.
Threat of Substitute products & Services
High – when there are many alternatives to a product or service.
Low – when there are few alternatives from which to choose.
-Ideally, an organization would like to be on a market in which there are few substitutes of their product or services.
-Best practices of IT
-E.g. Electronic product -same function different brands
Threat of new entrants
High – when it is easy for new competitors to enter a market.
Low – when there are significant entry barriers to entering a market.
-Entry barriers is a product or service feature that customers have come to expect from organizations and must be offered by entering organization to compete and survive.
Rivalry among existence competitors
High – when competition is fierce in a market
Low – when competition is more complacent
-Wal-mart and its suppliers using IT-enabled system for communication and track product at aisles by effective tagging system.
-Reduce cost by using effective supply chain.

The Three Generics Strategies
Cost leadership
-Becoming a low-cost producer in the industry allows the company to lower prices to customers.
-Competitors with higher costs cannot afford to compete with the low-cost leader on price.
Differentiation
-Create competitive advantage by distinguishing their products on one or more features important to their customers.
-Unique features or benefits may justify price differences and/or stimulate demand.
-Ex: i-care by Proton
The Value Chains- Targeting Business Processes
-Supply Chain - a chain or series of processes that adds value to product & service for customer.
-Add value to its products and services that support a profit margin for the firm
When there is a will, there is a way!
Our intuition about the future is linear. But the reality of information technology is exponential, and that makes a profound difference. If I take 30 steps linearly, I get to 30. If I take 30 steps exponentially, I get to a billion.





No comments:
Post a Comment